
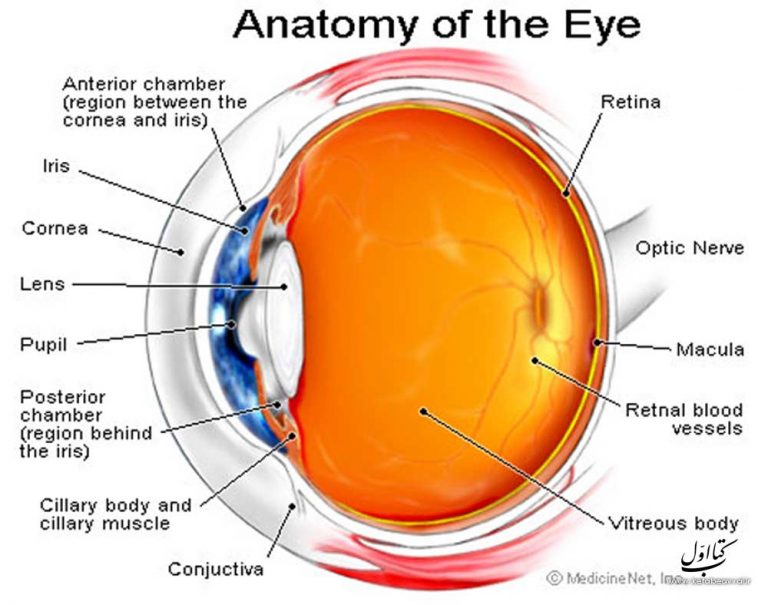
This ability to change focus for close-up objects is called accommodation. When you are looking at a near object, the lens needs to become more rounded at the central surface in order to focus the light rays. It is attached to the lens by zonules (ligament fibres that can be tight or loose). This ciliary muscle can change the shape of the crystalline lens by stretching it at the edges. The ciliary muscle is a circular ring of muscle that attaches all the way around the lens. It consists of a convex lens that is soft and pliable. The crystalline lens and accommodationīehind the aqueous fluid is the second lens system. These structures include the ciliary muscle, ciliary processes, ciliary vessels and ciliary epithelia. It is composed of several unique structures that give the ciliary body its unique shape and function. Wearing swimming goggles under water allows the layer of air to be present. The ciliary body is an inner eye structure, located at the border between the choroid and the iris. Things appear out of focus because the cornea is designed to work with light passing into it from air rather than from water. This becomes noticeable if you try to look at something when you are under water. If the change in refractive index was not as great, the light would not bend as much. Air has a refractive index of 1.00, and the aqueous fluid behind the cornea has a refractive index of 1.33. This bending is possible because of the curve of the cornea as well as the change in refractive index as light moves from air into the cornea and then into the aqueous fluid between the cornea and the iris. Contact Us: U.S.About 70% of the bending of light takes place as it enters the cornea and the aqueous fluid.Please contact the rights holder of this image for permission requests. Any use of this image is subject to prevailing copyright laws. The top panel shows outside of the eye including the eyelid, pupil, sclera, and iris the bottom panel shows inside of the eye including the cornea, lens, ciliary body, retina, choroid, optic nerve, and vitreous humor.Īnatomy of the eye, showing the outside and inside of the eye including the eyelid, pupil, sclera, iris, cornea, lens, ciliary body, retina, choroid, vitreous humor, and optic nerve.Ĭolor, Medical Illustration (JPEG format) The lens is the structure that changes shape to focus light on the retina.
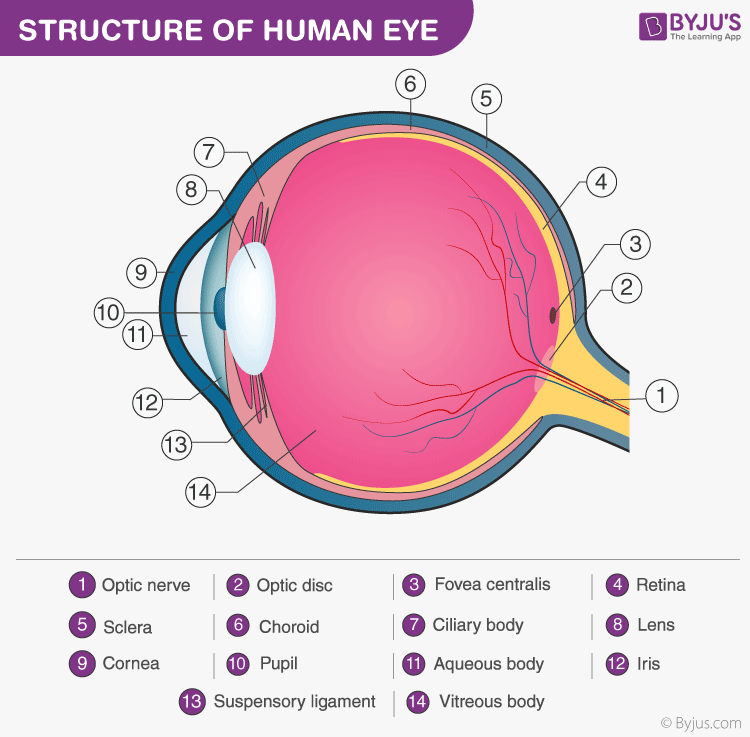
Eye anatomy two-panel drawing shows the outside and inside of the eye. Animation: Structure and Function of the Eye.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
